Advanced Alerts: Concepts & Visual Guide
This page introduces advanced alerting features, including event transformation, alert configuration, and bookmarking. Use the tabs and visual examples to master powerful monitoring and automation.
Quick Start
- Review the event transformation and alert config sections below.
- Use the code and screenshots in each tab as a reference for your setup.
- Explore advanced options for custom logic, global variables, and bookmarking.
Bookmark Settings & TimeSeries
Event Transformation Function
The event transformation function is a JavaScript function executed for each event before it is processed by the alert system. Use this function to:
This enables flexible, real-time enrichment of your event data.
Global Variables

Example transformation function
function addDuration(event) {
const etype = event?.attrs?.type;
if (etype === undefined) return;
if (etype === "reg-new" || etype === "reg-del" || etype === "reg-expired") {
event.attrs.fnc = event.attrs.from + "#" + event.attrs.contact;
}
if (etype === "call-attempt") {
// Example: set duration to 0 for call attempts
event.attrs.duration = 0;
} else if (etype === "reg-new") {
event.attrs.regdiff = 1;
event.attrs.regid = event.attrs.from + event.attrs["call-id"];
}
if (etype === "reg-del" || etype === "reg-expired") {
event.attrs.regdiff = -1;
event.attrs.regid = event.attrs.from + event.attrs["call-id"];
}
// Normalize index name by removing date
if (event?.metadataAA) {
event.metadataAA.fullIndex = event?.metadataAA?.index?.split("-")?.[0];
}
}
Be careful when modifying event attributes, as incorrect logic can lead to missed or false alerts.
💡 Tip: Use transformation functions to pre-process events for more effective alerting and analytics.
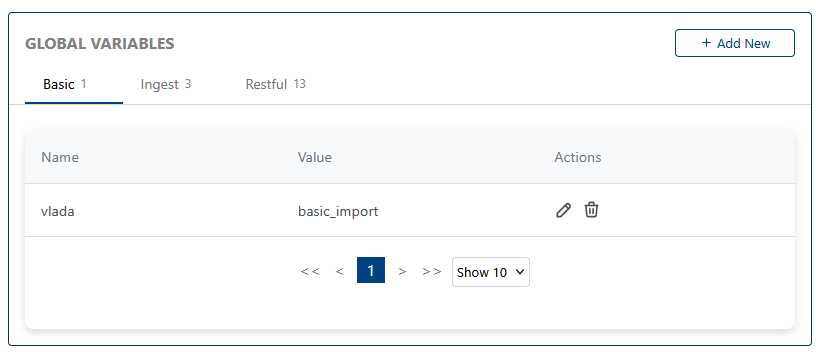
🌐 Global Variables
Global variables provide shared context and configuration for your alerting logic. These can be used to store reusable values, thresholds, or state across multiple alerts.
Alert Config
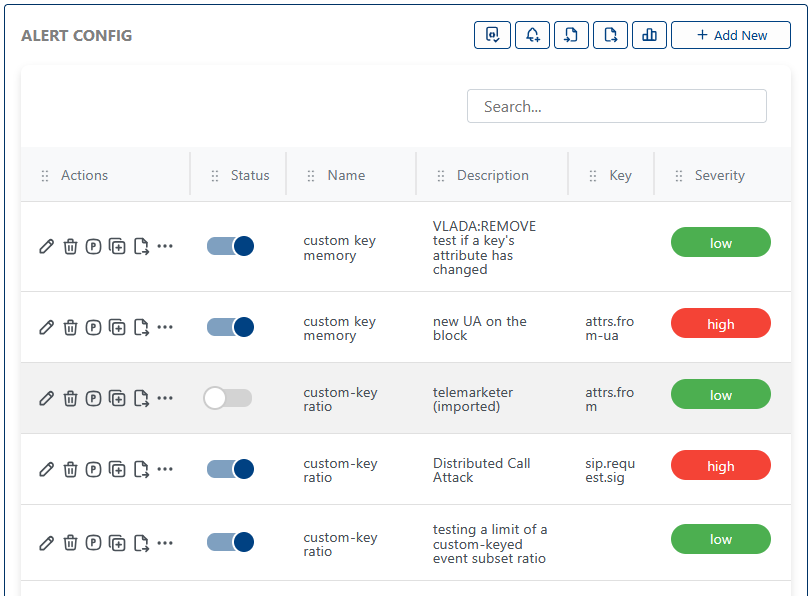
The alert configuration allows you to define how alerts are processed, including:
- The conditions that trigger an alert
- The actions to take when an alert is triggered
- Notification and escalation settings
Start with the overview below, then explore each configuration page in the tabs.
- Test Event
- Import Alert Config
- Import Configuration
- Example Alert Config JSON
- Global Alert Processing
Preview how a test event is processed and triggers alerts. Useful for debugging and validation.
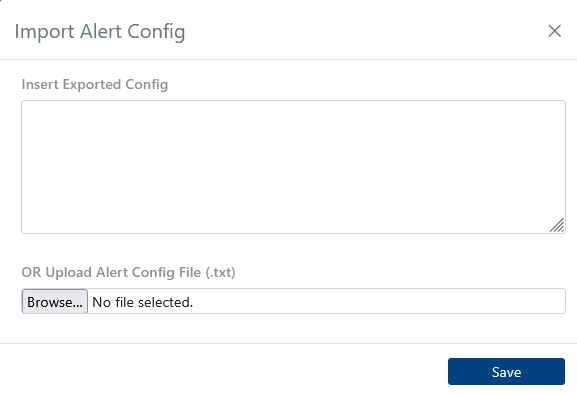
Import alert configurations from external sources to quickly set up or migrate alert rules.
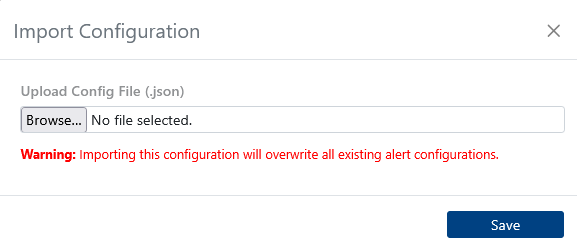
Import system-wide configuration settings for alerts and notifications.
Download or review a sample alert configuration JSON file for reference or bulk import. Below is a snippet from the file:
{
"ESvkpz_8": {
"name": "custom key memory",
"info": "See if an attribute is chaning in a keyed event stream",
"type": "CKM",
"enable": true,
"description": "VLADA:REMOVE test if a key's attribute has changed",
"parameters": {
"filter": { "value": "" },
"key": { "value": "" },
"keyMask": { "value": "" },
"ignore": { "value": 2 }
}
}
}
Visualize the global alert processing workflow and understand how events flow through the system.
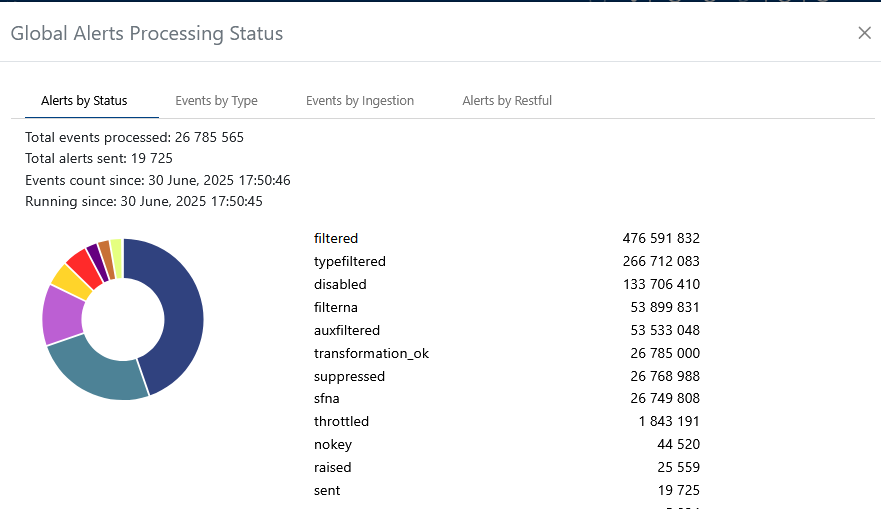
Adding a New Alert
Adding a new alert is simple and intuitive. Use the interface below to define your alert criteria, actions, and notification preferences. The screenshots in the tabs illustrate different alert types and advanced options.
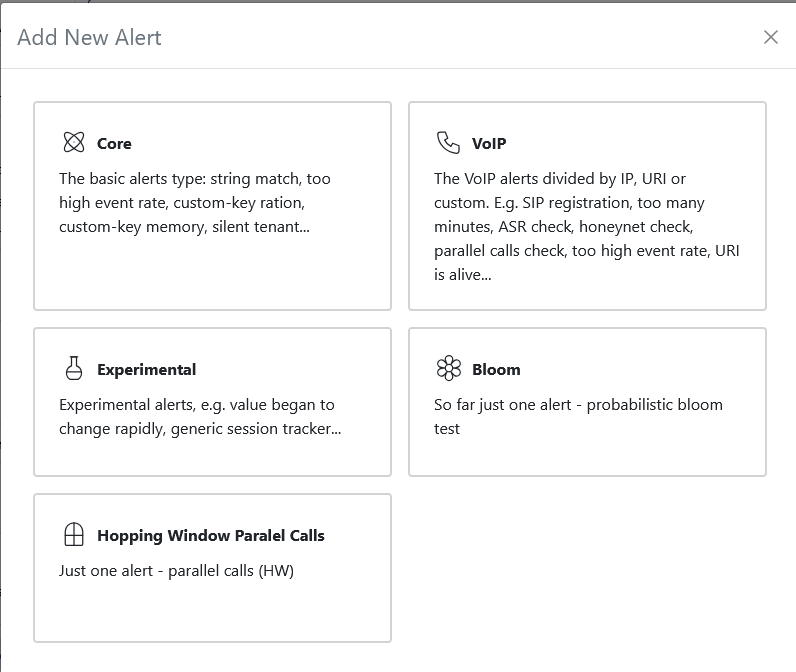
- Core Alert
- VoIP Alert
- Experimental Alert
- Bloom Alert
- Hopping Window Calls
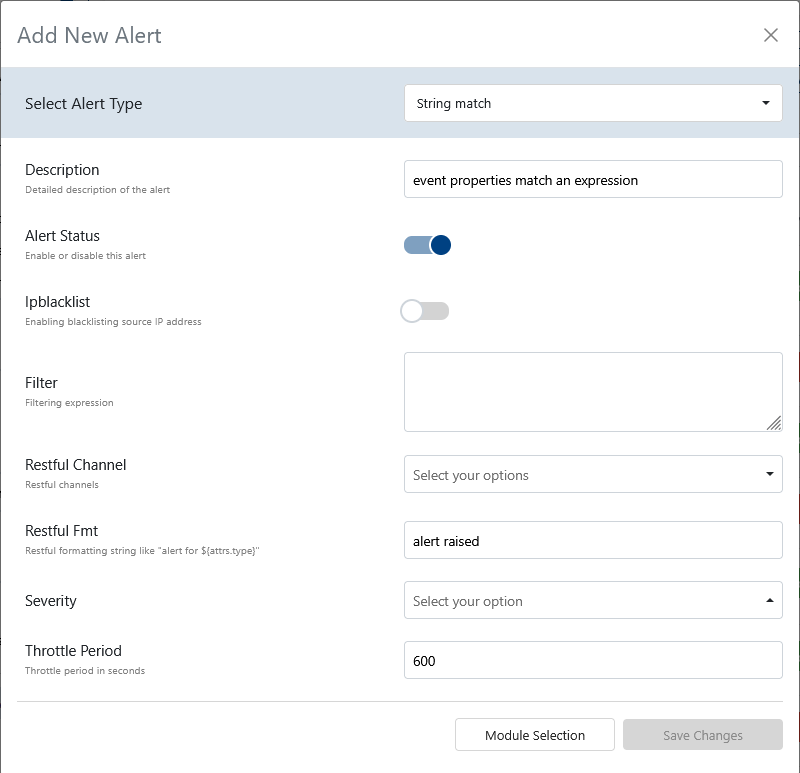
- Alert Type: Select from
string match,custom-key match,custom key memory,silent tenant,custom-key high rate, orcustom-key ratio. See Events Reference for event types. - Description: A human-readable explanation of what this alert does.
- Alert Status: Toggle to enable or disable the alert itself.
- IP BlackList: Toggle to enable or disable blacklisting of the source IP address when the alert triggers.
- Filter: Free-form text for a filtering expression to select relevant events.
- Restful Channel: Choose from a predefined list of RESTful notification channels.
- Restful FMT: Formatting string for RESTful notifications (e.g.,
alert for attrs.type). - Severity: Select the severity level:
high,medium,low, orinfo. - Throttle Period: Throttle period in seconds to limit alert frequency.
Adjust these fields to match your monitoring needs. For more on event attributes, see the Events Reference.
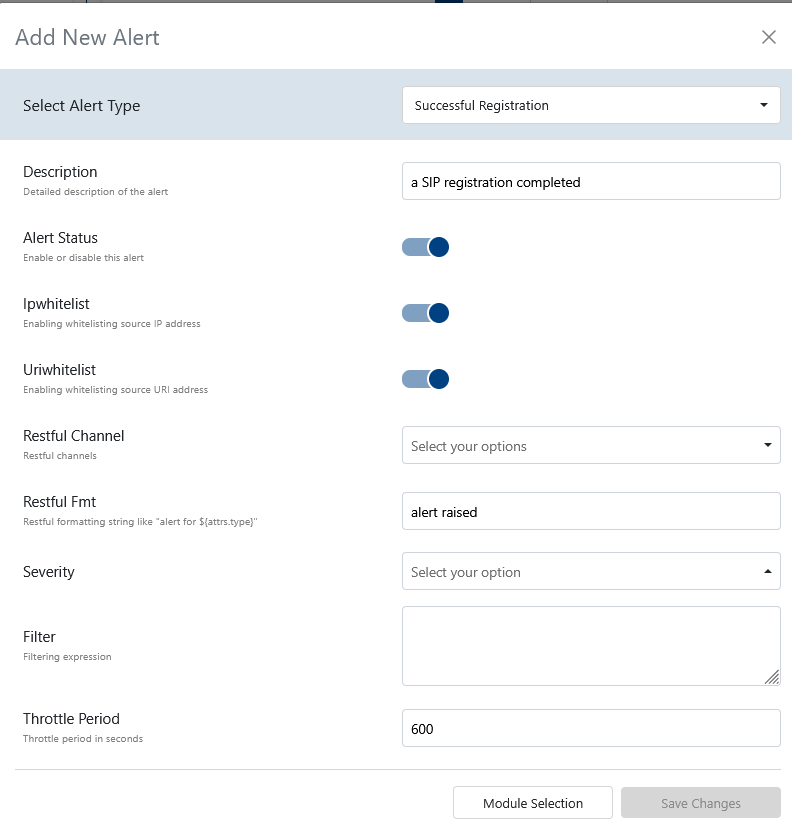
- Alert Type: Select from a comprehensive list, including
Successful Registration,Unknown User Agent,Unknown Subnet,Changed Country,Too many minutes from an IP,Too many minutes from a URI,Low Dst ASR,Low ASR,Honeynet,EvilUser Agent,Parallel Calls for a custom key,Parallel Calls for destination IP,Parallel Calls for URI,Parallel Calls for tenant,Late BYEs,Too Long Calls from an IP,Failing Authentications from a URI,Failing Authentications from an IP,URI many call attempts,IP many call attempts,URI custom ratio,Ratio,IP custom match ratio,From-URI high rate,Src/dst IP high rate,From/To URI high rate,To URI high rate,Uri Watch. See Events Reference for event types. - Description: A human-readable explanation of what this alert does.
- Alert Status: Toggle to enable or disable the alert itself.
- IP Whitelist: Toggle to enable whitelisting of source IP addresses.
- URI Whitelist: Toggle to enable whitelisting of source URI addresses.
- Restful Channel: Choose from a predefined list of RESTful notification channels.
- Restful FMT: Formatting string for RESTful notifications (e.g.,
alert for).${attrs.type} - Filter: Filtering expression to select relevant events.
- Severity: Select the severity level:
high,medium,low, orinfo. - Throttle Period: Throttle period in seconds to limit alert frequency.
Use these fields to monitor VoIP-specific issues. For event details, see the Events Reference.
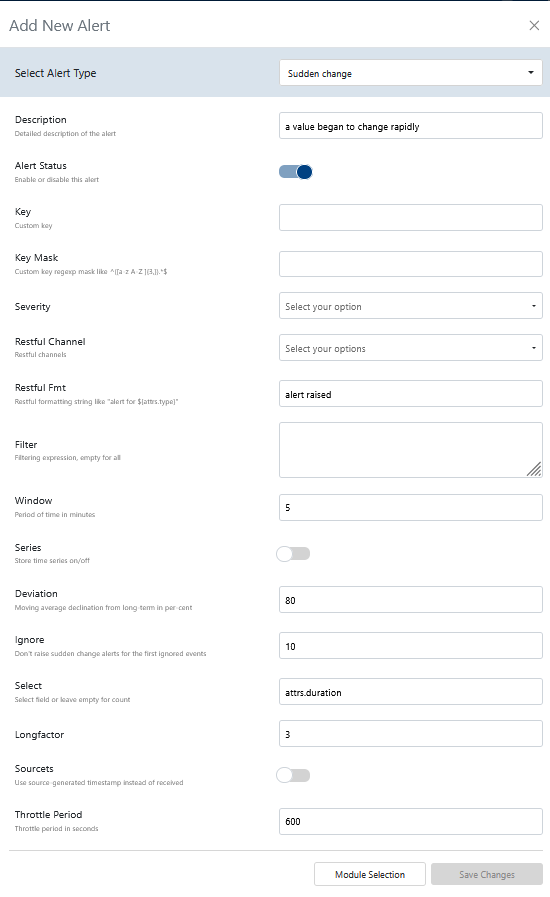
- Alert Type: Select from
sudden changes,parallel sessions for a custom key,value change, orz-score[1]. See Events Reference for event types. - Description: A human-readable explanation of what this alert does.
- Alert Status: Toggle to enable or disable the alert itself.
- Key: Custom key for grouping or identifying event streams.
- Key Mask: Custom key regexp mask (e.g.,
^([a-z A-Z ]{3,}).*$ - Severity: Select the severity level:
high,medium,low, orinfo. - Restful Channel: Choose from a predefined list of RESTful notification channels.
- Restful FMT: Formatting string for RESTful notifications (e.g.,
alert for).${attrs.type} - Filter: Filtering expression to select relevant events.
- Window: Period of time in minutes for the alert window.
- Series: Toggle to store time series data (on/off).
- Deviation: Moving average declination from long-term in percent.
- Ignore: Number of initial events to ignore before raising sudden change alerts.
- Select: Select field or leave empty for count.
- Longfactor: Long-term factor for moving average calculations.
- Sourcets: Toggle to use source-generated timestamp instead of received timestamp.
- Throttle Period: Throttle period in seconds to limit alert frequency.
Use experimental alerts to prototype new detection logic. Reference event types as needed.
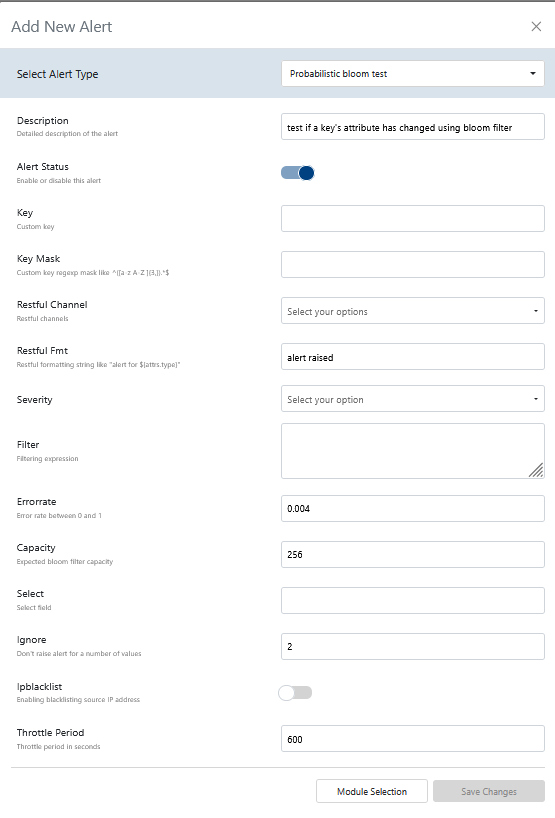
- Alert Type: Select from
probabilistic bloom test. See Events Reference for event types. - Description: A human-readable explanation of what this alert does.
- Alert Status: Toggle to enable or disable the alert itself.
- Key: Custom key for grouping or identifying event streams.
- Key Mask: Custom key regexp mask (e.g.,
^([a-z A-Z ]{3,}).*$ - Severity: Select the severity level:
high,medium,low, orinfo. - Restful Channel: Choose from a predefined list of RESTful notification channels.
- Restful FMT: Formatting string for RESTful notifications (e.g.,
alert for).${attrs.type} - Filter: Filtering expression to select relevant events.
- Errorrate: Error rate for the bloom filter (between 0 and 1).
- Capacity: Expected bloom filter capacity (number of unique items).
- Select: Select field or leave empty for count.
- Ignore: Number of values to ignore before raising an alert.
- IP Blacklist: Toggle to enable blacklisting of source IP address.
- Throttle Period: Throttle period in seconds to limit alert frequency.
Bloom alerts are for advanced, high-volume scenarios. See the Events Reference for event details.
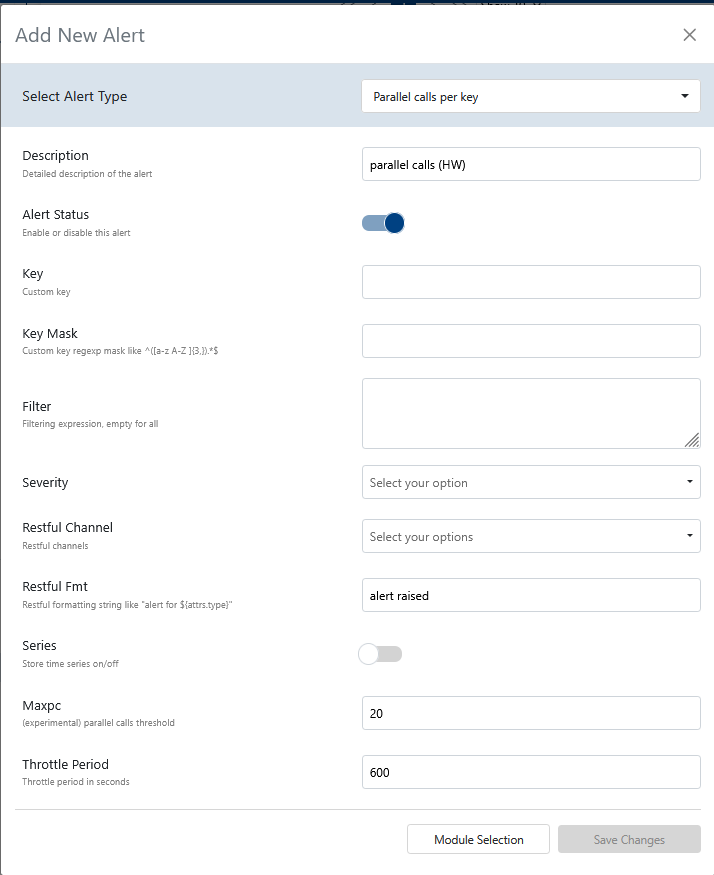
- Alert Type: Select from
parallel calls per key. See Events Reference for event types. - Description: A human-readable explanation of what this alert does.
- Alert Status: Toggle to enable or disable the alert itself.
- Key: Custom key for grouping or identifying event streams.
- Key Mask: Custom key regexp mask (e.g.,
^([a-z A-Z ]{3,}).*$ - Filter: Filtering expression to select relevant events.
- Severity: Select the severity level:
high,medium,low, orinfo. - Restful Channel: Choose from a predefined list of RESTful notification channels.
- Restful FMT: Formatting string for RESTful notifications (e.g.,
alert for).${attrs.type} - Series: Toggle to store time series data (on/off).
- maxpc: (Experimental) Parallel calls threshold.
- Throttle Period: Throttle period in seconds to limit alert frequency.
Use hopping window analytics to detect spikes in parallel calls. See the Events Reference for event details.
🔖 Bookmark Settings & TimeSeries
Bookmark settings allow you to save, organize, and quickly access important events or alert configurations. Use bookmarks to streamline your workflow and revisit key data points.
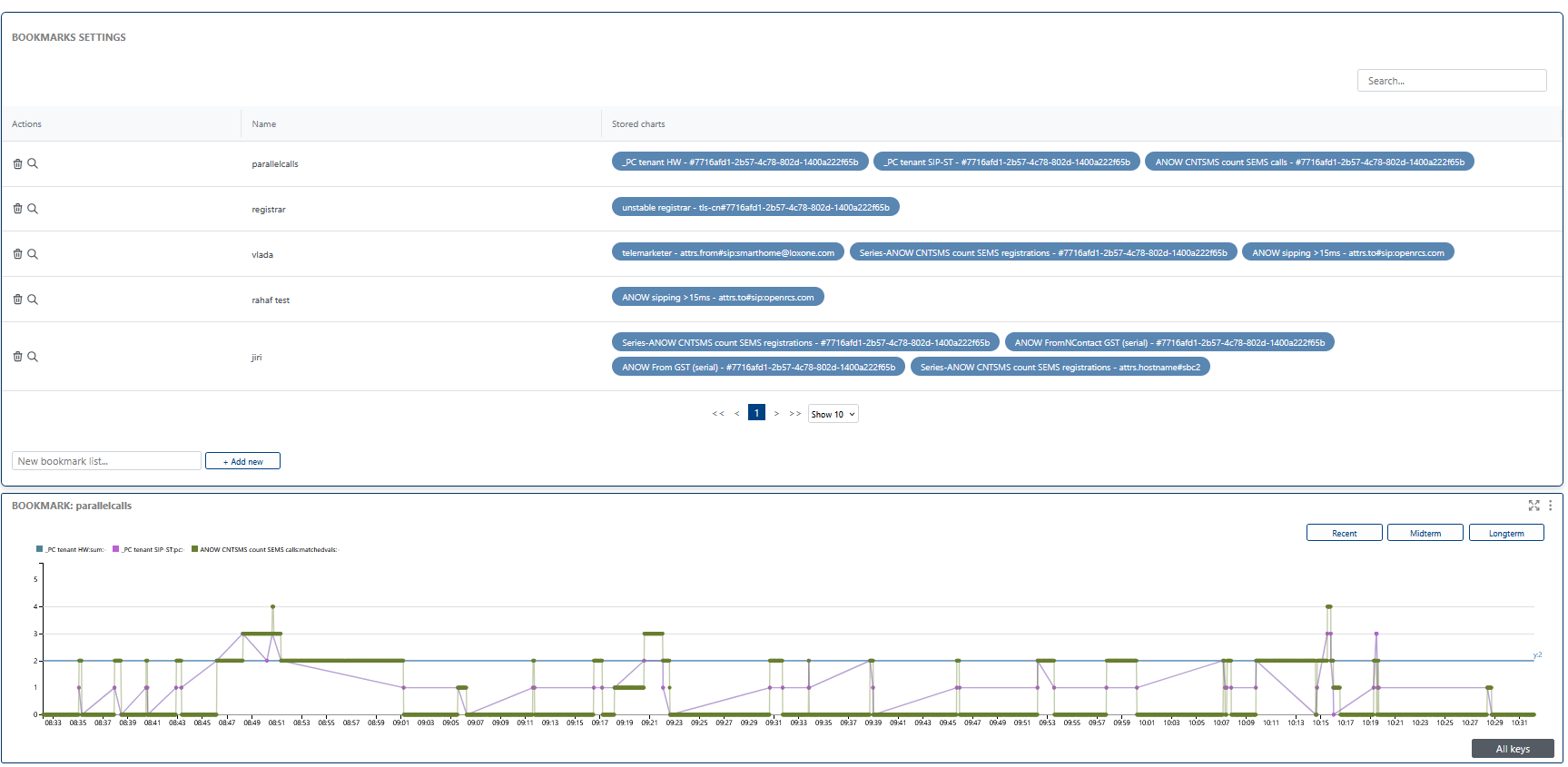
the TimeSeries section visualizes the data and events that you have bookmarked. You can access this visualization by clicking the magnifying glass icon next to a bookmark, providing a clear and interactive way to analyze trends, patterns, and anomalies over time. Use this visualization to gain deeper insights into your alert history and system behavior.
How It Works
- Ingestion: The system ingests incoming JSON events from various data sources (e.g., network equipment, SBCs).
- Stream Mapping: Events are mapped into streams using selected
keys(such as user, trunk, or IP). - Alert Evaluation: Each stream is checked against alerting criteria. If a threshold is exceeded, an alert is triggered.
- Notification/Automation: Alerts are pushed via RESTful plugins or other integrations.
For a detailed explanation of event types and their structure, see the Events Reference.
Footnotes
[1] Z-score is a statistical measure that describes how many standard deviations a data point is from the mean. In alerting, it is used to detect anomalies by identifying values that are unusually high or low compared to historical data. For example, a high z-score may indicate a sudden spike in call attempts or errors, triggering an alert for abnormal behavior.